In general, open source CSPM tools are safe to use. They are developed by a community of developers and undergo regular testing and updates to ensure their security and reliability. However, as with any software tool, it is important to take precautions to ensure the safety and security of your cloud infrastructure. This includes regularly updating the tool, monitoring its performance, and ensuring it is configured correctly.
Who should avoid using open source CSPM tools?
Not every organization may want to use an open source CSPM tool. Organizations that have strict compliance or regulatory requirements should avoid using open source tools as they may not meet specific regulatory standards. In addition, organizations with limited in-house technical expertise may struggle to implement and maintain an open source CSPM tool effectively. In these cases, it is more appropriate to use a commercial CSPM tool designed to meet specific regulatory requirements and backed by dedicated support and maintenance teams.
Now that you understand various CSPM solutions and the value they bring to the table, let us understand the Gartner Magic Quadrant and its importance in CSPM tool selection.
Understanding the Gartner Magic Quadrant
The Gartner Magic Quadrant is a research methodology used to evaluate and analyze technology markets, vendors, and products. The Magic Quadrant is a visual representation of the market, divided into four quadrants: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players. Each vendor is positioned in the quadrant that best represents their ability to execute their capabilities and showcase their completeness of vision in the market.
In the context of CSPM – or Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP), as they sometimes go hand in hand – the Magic Quadrant assesses the various vendors that offer CSPM solutions based on their capabilities and performance in the market. Gartner evaluates each vendor based on a variety of criteria, including product features and functionality, vendor strategy, customer experience, and market presence.
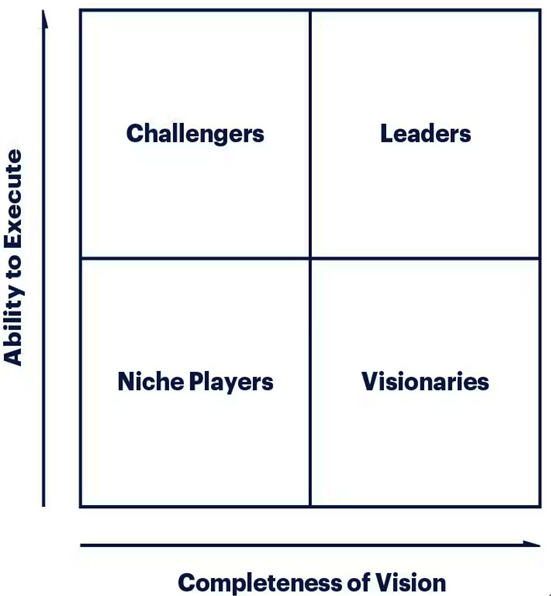
Figure 3.1 – Gartner Magic Quadrant (https://www.horangi.com/blog/a-cisos-take-on-the-gartner-magic-quadrant)
The Leaders quadrant would typically include vendors that have a strong market presence, a comprehensive CSPM product portfolio, and a proven record of accomplishment of delivering customer value. The Challengers quadrant includes vendors that may have a strong product portfolio but may be lacking in certain areas such as market presence or innovation. The Visionaries quadrant includes vendors that have a strong vision for the future of CSPM but may be lacking in execution. The Niche Players quadrant includes vendors that have a smaller market presence or a more limited product portfolio.
Overall, the Magic Quadrant provides a valuable resource for organizations looking to evaluate and compare CSPM solutions. It can help organizations identify leading vendors in the market, evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, and select the CSPM tool that best meets their specific needs and requirements.
